Table of Contents
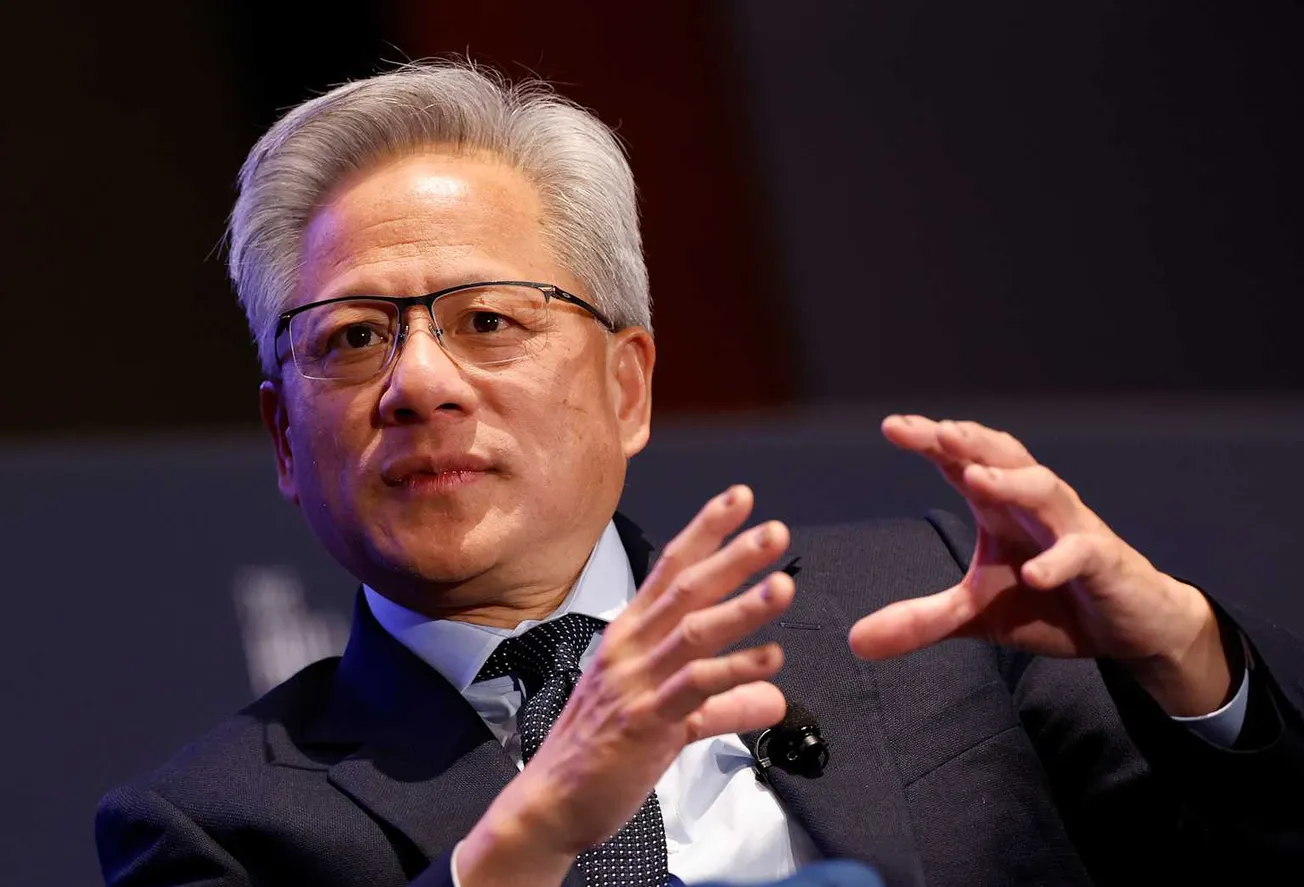
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang warns that being locked out of China’s rapidly expanding AI chip market-projected to reach $50 billion-would be a significant setback for US innovation, jobs, and revenue.
Key Takeaways
- China’s AI chip market is projected to reach $50 billion in the next 2–3 years.
- Nvidia CEO warns that exclusion from China would be a “tremendous loss” for US companies, jobs, and tax revenue.
- Export restrictions have already cost Nvidia $5.5 billion in writedowns related to its H20 chip.
- Nvidia is actively lobbying against tighter US restrictions and tweaking chip designs to comply with export rules.
- Chinese competitors like Huawei are developing alternatives, threatening Nvidia’s market share in China.
The Rise of China’s AI Chip Market
The artificial intelligence sector in China is experiencing unprecedented growth, with the market for AI chips alone expected to hit $50 billion within the next two to three years. Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang has repeatedly emphasized the importance of this market, calling it “crucial for US companies” to gain access. In a recent CNBC interview, Huang underscored the scale of the opportunity: “China is a very large market... It would be a tremendous loss not to be able to address it as an American company”.
China’s Big Tech firms-including Tencent Holdings and ByteDance-are among the largest consumers of these chips, using them to develop and train advanced AI models. The sheer size and dynamism of this market make it an essential battleground for global tech leaders, especially as AI becomes a cornerstone of economic and technological competition worldwide.
The Impact of US Export Restrictions
Despite the immense potential, Nvidia and other US chipmakers face mounting challenges due to tightening export controls. The US government, under both the Biden and Trump administrations, has imposed multiple rounds of restrictions on the sale of high-performance AI chips to China. These measures are intended to protect national security by limiting China’s access to cutting-edge technology.
The latest round of restrictions specifically targets Nvidia’s H20 AI chip, a product designed for the Chinese market to comply with earlier export rules. As a result, the company was forced to take a $5.5 billion writedown and now requires special approval to ship the H20 to Chinese customers. Huang has warned that these policies could ultimately undermine US national security by weakening American companies’ competitive edge and driving Chinese firms to develop their own alternatives.
Nvidia’s Strategic Response: Agility and Advocacy
In response to these challenges, Nvidia is pursuing a dual strategy of compliance and advocacy. The company is actively tweaking the design of its AI chips to meet evolving export requirements, ensuring it can continue serving Chinese customers-at least for now. Huang has personally visited China to reassure major clients like Alibaba, ByteDance, and Tencent that Nvidia remains committed to the market.
At the same time, Huang is lobbying US policymakers to reconsider tighter restrictions, arguing that blocking American companies from China’s AI chip market will harm US innovation, tax revenue, and job creation. “It’s going to bring back revenues. It’s going to bring back taxes. It’s going to create lots of jobs here in the United States,” he told CNBC.
Huang’s message is clear: “Let Americans do American-let us go after it and win it.” He believes that the US should lead in AI by allowing its companies to compete globally, rather than retreating from the world’s largest semiconductor market.
The Rise of Chinese Competitors
The uncertainty created by US export controls is accelerating the emergence of homegrown Chinese alternatives. Companies like Huawei are rapidly advancing their own AI chips, such as the Ascend 910D, which is seen as a direct competitor to Nvidia’s flagship H100 GPU. With US restrictions limiting access to Nvidia and AMD products, Chinese tech giants are increasingly turning to domestic solutions, threatening to erode Nvidia’s dominance in the region.
This trend is not lost on Huang, who has acknowledged Huawei as “one of the most formidable companies in the world.” The risk, he suggests, is that US policies intended to protect American interests may inadvertently spur China’s technological self-sufficiency and reduce the global influence of US firms.
Economic and Strategic Implications
The stakes are high for both Nvidia and the broader US economy. China accounted for roughly 14% of Nvidia’s revenue last year-about $17.1 billion-and the company’s fortunes have been closely tied to the global AI boom. Losing access to the Chinese market would not only dent Nvidia’s bottom line but also impact US tax receipts and job creation, as Huang has repeatedly emphasized.
Moreover, the broader implications for US technological leadership are significant. By restricting exports, the US risks ceding ground to Chinese innovators and weakening its own position in the global AI race. Huang’s warning is stark: “It would be a tremendous loss not to be able to address [China’s AI market] as an American company”.
Conclusion
Nvidia’s struggle to navigate US-China trade tensions highlights the complex interplay between national security, economic opportunity, and technological innovation. As China’s AI chip market surges toward $50 billion, the choices made by US policymakers will have far-reaching consequences for American companies, workers, and the country’s standing in the global tech race. For now, Nvidia remains committed to staying agile and advocating for a path forward that allows US firms to compete-and win-on the world stage